Help is available for individuals who struggle with opioid use disorder. There are numerous resources and support systems in place to assist individuals in overcoming addiction and achieving recovery. By taking steps and actively engaging in the recovery process, individuals can overcome opioid use disorder and build a fulfilling life free from addiction.

Websites
SAMHSA’s National Helpline
SAMHSA's National Helpline is a free, confidential, 24/7, 365-day-a-year treatment referral and information service (in English and Spanish). Call 1-800-662-HELP (4357) or visit the website.
988 Suicide & Crisis Lifeline – Call. Text. Chat.
The 988 Lifeline provides 24/7, free and confidential support for people in distress, prevention and crisis resources for you or your loved ones, and best practices for professionals in the United States.
Behavioral Health Nevada
This website is a database of behavioral health providers in Nevada specializing in substance use disorder and co-occurring mental health disorder treatment services. All agencies listed are Certified by the Division, SAPTA (Substance Abuse Prevention and Treatment Agency).
Crisis Support Services of Nevada
Crisis Support Services of Nevada provides 24/7, free, confidential and caring support to people in crisis.
Stop Overdose
To address the increasing number of overdose deaths related to both prescription opioids and illicit drugs, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) created a website to educate people who use drugs about the dangers of illicitly manufactured fentanyl, the risks and consequences of mixing drugs, the lifesaving power of naloxone, and the importance of reducing stigma around recovery and treatment options.
Tools & Resources
Nevada Fentanyl Test Strip Distribution Sites
A list and map of Fentanyl Test Strip Distribution Sites in Nevada.
Nevada Overdose Reversal Medication Finder
Find naloxone and overdose reversal medications in Nevada.
Behavioral Health Nevada
This website is a database of behavioral health providers in Nevada specializing in substance use disorder and co-occurring mental health disorder treatment services. All agencies listed are Certified by the Division, SAPTA (Substance Abuse Prevention and Treatment Agency).
How to Use Fentanyl Test Strips
Infographics and step-by-step instructions.
Never Use Alone
Toll-free national overdose prevention, detection, life-saving crisis response and medical intervention services for people who use drugs while alone. Never Use Alone’s peer operators are available 24-hours a day, 7 days a week, 365 days a year.
PACT Coalition
The PACT Coalition seeks to empower Southern Nevada with the resources to prevent substance misuse for all ages and promote recovery through culturally competent advocacy, education, stigma reduction, support, and outreach. A diverse cross-section of community leadership is represented by the PACT Coalition that will work together to ensure a sustainable future and a healthier community. PACT Coalition keeps an updated resource list for Southern Nevada.
Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT) for Opioid Use Disorder
SAMHSA offers a guide on MAT for opioid use disorder, which includes information on the various medications available for treatment, as well as resources for finding MAT providers and programs.
Referrals/Funded Providers
Treatment and recovery options are available in Nevada and are continually expanding. These options include medication assisted treatment (MAT), peer support, case management, comprehensive services for pregnant patients, counseling, educational classes, and wrap-around services.
Overdose Reversal Medication for Individuals & Families
Guides to opioid safety and how to use overdose reversal medications.
Know Your Pain Meds
Provides information on how opioids work, alternatives to pain medicine, the overdose reversal medication naloxone, a substance use disorder treatment finder, and submit concerns you have about a medical provider.
Overdose Prevention and Response Toolkit
This toolkit provides guidance to a wide range of individuals on preventing and responding to an overdose. The toolkit also emphasizes that harm reduction and access to treatment are essential aspects of overdose prevention.
Storage and Disposal of Medication
Improper prescription drug use is a serious public health issue. Storing and disposing of medications properly can help reduce harm.
Posters & Infographics

Opioid Trifold Brochures
Opioid Information Brochures for Providers or Consumers help educate on opioids and opioid use, including effects of opioid use, pregnancy and opioid use, medications for opioid use including opioid overdose reversal medications, and treatment options for persons using opioids.
Download or request free hard copies

Stimulant Trifold Brochures
Stimulant Information Brochures for Providers or Consumers help educate on stimulants, including the effects of stimulants use, pregnancy and stimulant use, and treatment options for persons using stimulants.
Download or request free hard copies

Prevent Addiction Fact Sheet
This face sheet contains information for patients about preventing opioid addiction.
Download the fact sheet.

Opioid Use Disorder Treatment and Recovery Fact Sheet
This fact sheet contains important information about treatment and recovery of opioid use disorder for patients, families and friends.
Download the fact sheet
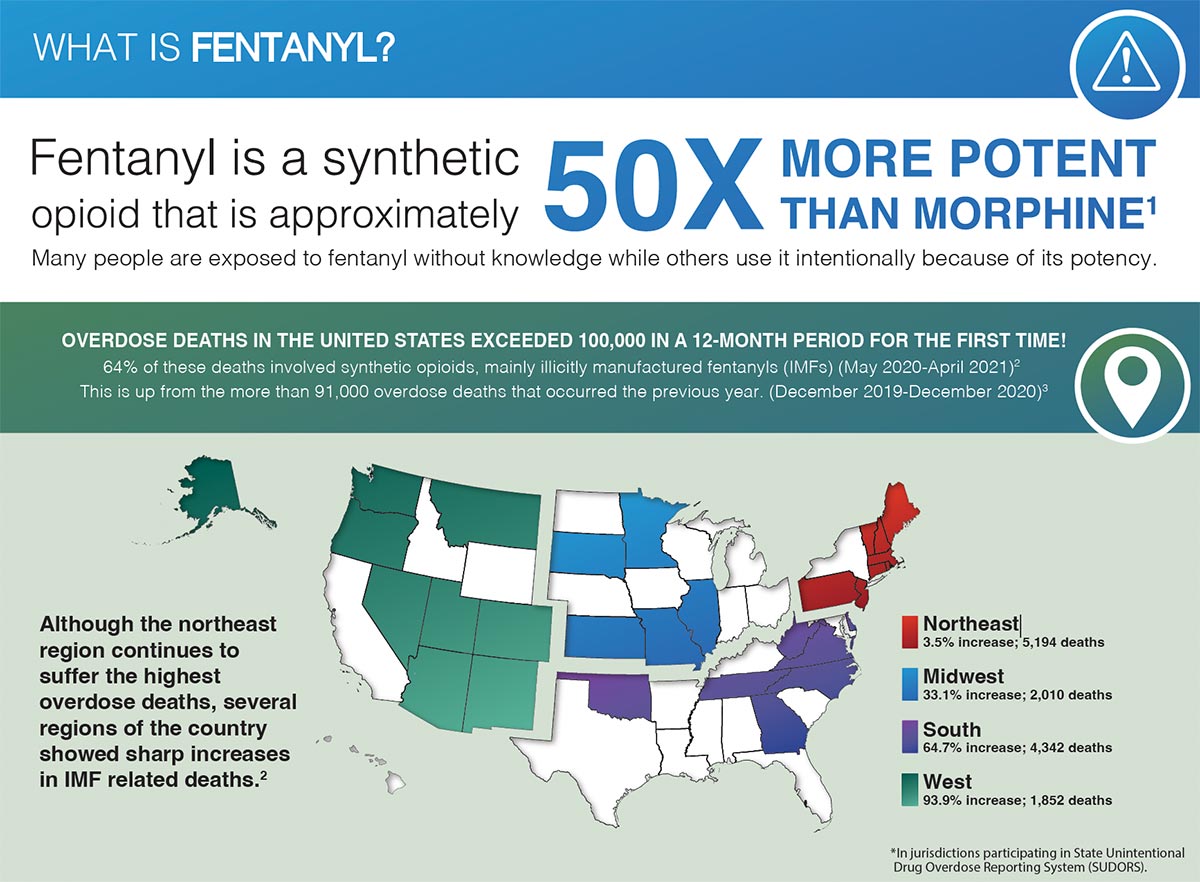
What is Fentanyl? Infographic
This infographic was developed by the National Institute on Drug Abuse.
Download the infographic

Medications for Opioid Use Disorder (MOUD) Infographic
This infographic shows different types of medications approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for opioid overdose, withdrawal, and addiction.
Download the infographic
Publications
Beyond Addiction: How Science and Kindness Help People Change
The most innovative leaders in progressive addiction treatment in the US offer a groundbreaking, science-based guide to helping loved ones overcome addiction problems and compulsive behaviors.
SAMHSA – Recovery and Recovery Support
This publication by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) provides comprehensive information on recovery-oriented systems of care for individuals with substance use disorders, including opioid use disorder. It includes resources for individuals seeking recovery support services.
Facing Addiction in America: The Surgeon General’s Spotlight on Opioids
This publication by the Office of the Surgeon General provides an overview of the opioid epidemic in the United States and offers resources for individuals, families, and communities affected by opioid use disorder.
In My Own Words
A compilation of essays by individuals supported by Medication-Assisted Treatment in long-term recovery.
Webinars & Online Learning
Current News & Research
DEA Reports Widespread Threat of Fentanyl Mixed with Xylazine
WASHINGTON - The U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration is warning the American public of a sharp increase in the trafficking of fentanyl mixed with xylazine. Xylazine, also known as “Tranq,” is a powerful sedative that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved for veterinary use.
The Opioid Epidemic’s Toll on Children
This article from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health discusses the opioid epidemics toll on children.
